Table of content
Union Budget 2024 at a glance
The Union Budget was announced on 23rd July 2024 by FM Nirmala Sitharaman. Being the first budget after the formation of the Government, this was a much awaited and speculated budget. With so much buzz around the budget, there was prone to a post-budget effect on the share market.
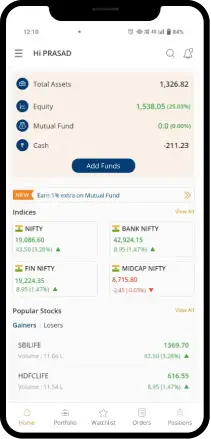
Let us quickly look at how the markets behaved post budget.
The increase in the rate of long-term capital gains tax and STT on Futures & Options caused the Sensex to plunge by 1.25% in a matter of just 15 minutes.
However, markets recovered just as quickly with Sensex closing 0.09% down while Nifty 50 ended in the red by just 0.12%.
Here are the top highlights from Budget 2024
-
Budget & Direct Taxation
-
Tax relief for salaried class, under the new tax regime:
-Standard deduction limit increased to ₹75,000 from ₹50,000
-Revised tax slabs
Tax Slab New Tax Rate Old Tax Rate 0-3 lakh - - 3-7 lakh 5% 5% 7-10 lakh 10% 10% 10-12 lakh 15% 15% 12-15 lakh 20% 20% Above 15 lakh 30% 30% With these reliefs, salaried employees now stand to save ₹17,500 on income tax.
-
Long-term capital gains tax raised to 12.5% from 10%:
-Effective today (23rd July 2024), the LTCG tax of 12.5% will be applicable over and above ₹1.25 lakh (exemption limit raised from ₹1 lakh) on equity shares and mutual funds.
-For other financial assets, including bonds and debentures, LTCG has been reduced to 12.5% (20% earlier), and there will be no indexation benefit
-Indexation benefit on long-term capital gains computation has been done away with. This means LTCG on property, gold and other unlisted assets will not be computed on indexed cost of acquisition of the asset.
-Short term capital gains (STCG) tax on equity shares and equity mutual funds has been raised to 20% from 15%
-
Securities transaction tax hiked
New STT Old STT Options 0.1% 0.0625% Futures 0.02% 0.0125% - Income received from share buybacks to be taxed from the investors.
- Corporate tax rate on foreign companies has been reduced to 35% from the earlier 40%.
- Angel tax, introduced in 2012, has been abolished in a bid to support the Indian startup ecosystem.
-
Tax relief for salaried class, under the new tax regime:
Indirect taxation
Basic customs duty on gold and silver has been reduced to 6% and on platinum it has been reduced to 6.4%.
Basic customs duty on imports of printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) has been increased to 15% from the earlier 10% to promote local manufacturing.
-
Other sectoral mandates:
- The Government has announced 5 key schemes with an outlay of ₹2 lakh crore to facilitate employment, skilling and other opportunities for 4.1 crore youth over a 5-year period,
- ₹1.52 lakh crore has been allocated for Agriculture and allied sectors
- Under, PM Awas Yojana 2.0 (Urban), ₹3,000 crore has been allocated for low-income group and ₹1,000 crore for Middle income group.
- The infrastructure sector receives an allocation of ₹11.11 lakh crore in a bid to boost capex that in turn will create job opportunities across construction, transport and logistics.